Alfa Kentauri
 Alfa Kentauri AB je najsvetlija zveza vidljiva s leve strane, koja formira trozvezdani sistem sa Proksima Kentauri, zaokruženom crveno. Najsvetliji zvezdani sistem sa desne strane je Beta Kentauri. | |
| Opservacioni podaci Epoha J2000.0 Ravnodnevnica J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Sazvežđe | Kentauri |
| Alfa Kentauri A | |
| Rektascenzija | 14h 39m 36.49400s[1] |
| Deklinacija | −60° 50′ 02.3737″[1] |
| Prividna magnituda (V) | +0.01[2] |
| Alfa Kentauri B | |
| Rektascenzija | 14h 39m 35.06311s[1] |
| Deklinacija | −60° 50′ 15.0992″[1] |
| Prividna magnituda (V) | +1.33[2] |
| Karakteristike | |
| A | |
| Spektralni tip | G2V[3] |
| U−B indeks boja | +0.24[2] |
| B−V indeks boja | +0.71[2] |
| B | |
| Spektralni tip | K1V[3] |
| U−B indeks boja | +0.68[2] |
| B−V indeks boja | +0.88[2] |
| Astrometrija | |
| A | |
| Radijalna brzina (Rv) | −21,4±0,76[4] km/s |
| Sopstveno kretanje (μ) | RA: −3679.25[1] mas/g Dek.: 473.67[1] mas/g |
| Paralaksa (π) | 754.81 ± 4.11[1] mas |
| Rastojanje | 4.37[5] sg |
| Apsolutna magnituda (MV) | 4.38[6] |
| B | |
| Radijalna brzina (Rv) | −18,6±1,64[4] km/s |
| Sopstveno kretanje (μ) | RA: −3614.39[1] mas/g Dek.: 802.98[1] mas/g |
| Paralaksa (π) | 754.81 ± 4.11[1] mas |
| Rastojanje | 4.37[5] sg |
| Apsolutna magnituda (MV) | 5.71[6] |
| Detalji | |
| Alfa Kentauri A | |
| Masa | 1.100[7] M☉ |
| Poluprečnik | 1,2234±0,0053[8] R☉ |
| Luminoznost | 1.519[7] L☉ |
| Površinska gravitacija (log g) | 4.30[9] cgs |
| Temperatura | 5,790[7] K |
| Metaličnost [Fe/H] | 0.20[7] dex |
| Rotacija | 22±5,9 d[10] |
| Rotaciona brzina (v sin i) | 2,7±0,7[10] km/s |
| Alfa Kentauri B | |
| Masa | 0.907[7] M☉ |
| Poluprečnik | 0,8632±0,0037[8] R☉ |
| Luminoznost | 0.5002[7] L☉ |
| Površinska gravitacija (log g) | 4.37[9] cgs |
| Temperatura | 5,260[7] K |
| Metaličnost | 0.23[7] |
| Rotacija | 36[11] days |
| Rotaciona brzina (v sin i) | 1,1±0,8[12] km/s |
| Starost | 5,3±0,3[13] Gyr |
| Orbita[14] | |
| Primarna | A |
| Kompanjon | B |
| Period (P) | 79,91±0,011 g |
| Velika poluosa (a) | 17,57±0,022″ |
| Ekscentricitet (e) | 0,5179±0,00076 |
| Inklinacija (i) | 79,205±0,041° |
| Longituda uzlaznog čvora (Ω) | 204,85±0,084° |
| Apsidna epoha (T) | 1875,66±0,012 |
| Argument perihela (ω) (sekundarni) | 231,65±0,076° |
| Druge oznake | |
| α Cen A: Rigil Kentaurus, Rigil Kent, α1 Centauri, HR 5459, HD 128620, GCTP 3309.00, LHS 50, SAO 252838, HIP 71683 | |
| α Cen B: Toliman, α2 Centauri, HR 5460, HD 128621, LHS 51, HIP 71681 | |
| Referentne baze podataka | |
| SIMBAD | AB |
| A | |
| B | |
| Ekstrasolarna arhiva | data |
| ARICNS | data |
| Enciklopedija ekstrasolarnih planeta | data |
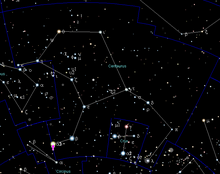
Alfa Kentauri ili α Cen ili Toliman je najsjajnija zvezda u sazvežđu Kentaur (Centaurus), koje je vidljivo od januara do jula, a kulminira tokom aprila i nije vidljivo sa severne polulopte na geografskim širinama većim od 30°. Alfa Kentaur je Zemlji najbliža zvezda, posle Sunca.
Iako je najbliža zvezda Zemlji (posle Sunca) tek je peta po sjaju sa svojom prividnom magnitudom 0,06, a nalazi se na 4,3 svetlosne godine od Zemlje. Koordinate Alfa Kentaura u sfernom nebeskom ekvatorskom koordinatnom sistemu su 14 sati i 36 minuta (rektascenzija) i -60°38' (deklinacija). Ova zvezda pripada spektralnoj klasi G2 (prema Harvardskoj spektralnoj klasifikaciji), kao i Sunce.
Alfa Kentauri je trojni sistem, čiji član je i Proksima Kentauri, najbliža zvezda Suncu.
Procene rastojanja
[uredi | uredi izvor]| Izvor | Paralaksa (mas) | Rastojanje (pc) | Rastojanje (ly) | Rastojanje (Pm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henderson (1839) | 1160±110 | 0,86+0,09 −0,07 |
2.57 ± 0.53 | 26,6+2,8 −2,3 |
[15] |
| Henderson (1842) | 912,8±64 | 1.03 ± 0.15 | 3.34 ± 0.5 | 33,8+2,5 −2,2 |
[16] |
| Maklir (1851) | 918,7±34 | 1,09±0,04 | 3,55+0,14 −0,13 |
32.4 ± 2.5 | [17] |
| Moesta (1868) | 880±68 | 1,14+0,10 −0,08 |
3,71+0,31 −0,27 |
35,1+2,9 −2,5 |
[18] |
| Gil & Elkin (1885) | 750±10 | 1,333±0,018 | 4,35±0,06 | 41,1+0,6 −0,5 |
[19] |
| Roberts (1895) | 710±50 | 1.32 ± 0.2 | 4.29 ± 0.65 | 43,5+3,3 −2,9 |
[20] |
| Vuli et al. (1970) | 743±7 | 1,346±0,013 | 4,39±0,04 | 41,5±0,4 | [21] |
| Glis & Jahreib (1991) | 749,0±4,7 | 1,335±0,008 | 4,355±0,027 | 41,20±0,26 | [22] |
| van Altena et al. (1995) | 749,9±5,4 | 1,334±0,010 | 4,349+0,032 −0,031 |
41,15+0,30 −0,29 |
[23] |
| Periman et al. (1997) (A and B) | 742,12±1,40 | 1,3475±0,0025 | 4,395±0,008 | 41,58±0,08 | [24] |
| Sederhjelm (1999) | 747,1±1,2 | 1,3385+0,0022 −0,0021 |
4,366±0,007 | 41,30±0,07 | [28] |
| van Liuven (2007) (A) | 754,81±4,11 | 1,325±0,007 | 4,321+0,024 −0,023 |
40,88±0,22 | [29] |
| van Liuven (2007) (B) | 796,92±25,90 | 1,25±0,04 | 4,09+0,14 −0,13 |
37.5 ± 2.5 | [30] |
| RECONS TOP100 (2012) | 747,23±1,17[note 2] | 1,3383±0,0021 | 4,365±0,007 | 41,29±0,06 | [31] |
Napomene
[uredi | uredi izvor]- ^ Proxima Centauri is gravitationally bound to the α Centauri system, but for practical and historical reasons it is described in detail in its own article.
- ^ Weighted parallax based on parallaxes from van Altena et al. (1995) and Söderhjelm (1999).
Reference
[uredi | uredi izvor]- ^ a b v g d đ e ž z i Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). „Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction”. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653—664. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. arXiv:0708.1752
 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- ^ a b v g d đ Ducati, J. R. (2002). „VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system”. CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237: 0. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ^ a b Torres, C. A. O.; Quast, G. R.; da Silva, L .; de la Reza, R.; Melo, C. H. F.; Sterzik, M. (2006). „Search for associations containing young stars (SACY)”. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 460 (3): 695—708. Bibcode:2006A&A...460..695T. ISSN 0004-6361. arXiv:astro-ph/0609258
 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065602.
. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065602.
- ^ a b Valenti, Jeff A.; Fischer, Debra A. (2005). „Spectroscopic Properties of Cool Stars (SPOCS). I. 1040 F, G, and K Dwarfs from Keck, Lick, and AAT Planet Search Programs”. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 159 (1): 141—166. Bibcode:2005ApJS..159..141V. ISSN 0067-0049. doi:10.1086/430500
 .
.
- ^ a b Wilkinson, John (2012). „The Sun and Stars”. New Eyes on the Sun
 . Astronomers' Universe. str. 219–236. ISBN 978-3-642-22838-4. ISSN 1614-659X. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-22839-1_10.
. Astronomers' Universe. str. 219–236. ISBN 978-3-642-22838-4. ISSN 1614-659X. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-22839-1_10.
- ^ a b P. A. Wiegert; M. J. Holman (1997). „The stability of planets in the Alpha Centauri system”. The Astronomical Journal. 113: 1445 — 1450. Bibcode:1997AJ....113.1445W. arXiv:astro-ph/9609106
 . doi:10.1086/118360.
. doi:10.1086/118360.
- ^ a b v g d đ e ž Thévenin, F.; Provost, J.; Morel, P.; Berthomieu, G.; Bouchy, F.; Carrier, F. (2002). „Asteroseismology and calibration of alpha Cen binary system”. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 392: L9. Bibcode:2002A&A...392L...9T. arXiv:astro-ph/0206283
 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021074.
. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021074.
- ^ a b Kervella, P.; Bigot, L.; Gallenne, A.; Thévenin, F. (januar 2017). „The radii and limb darkenings of α Centauri A and B. Interferometric measurements with VLTI/PIONIER”. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 597. A137. Bibcode:2017A&A...597A.137K. arXiv:1610.06185
 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201629505.
. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201629505.
- ^ a b Gilli G.; Israelian G.; Ecuvillon A.; Santos N. C.; Mayor M. (2006). „Abundances of Refractory Elements in the Atmospheres of Stars with Extrasolar Planets”. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 449 (2): 723—36. Bibcode:2006A&A...449..723G. arXiv:astro-ph/0512219
 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053850. libcode 2005astro.ph.12219G.
. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053850. libcode 2005astro.ph.12219G.
- ^ a b Bazot, M.; et al. (2007). „Asteroseismology of α Centauri A. Evidence of rotational splitting”. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 470 (1): 295—302. Bibcode:2007A&A...470..295B. arXiv:0706.1682
 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065694.
. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065694.
- ^ DeWarf, L.; Datin, K.; Guinan, E. (2010). „X-ray, FUV, and UV Observations of α Centauri B: Determination of Long-term Magnetic Activity Cycle and Rotation Period”. The Astrophysical Journal. 722 (1): 343—357. Bibcode:2010ApJ...722..343D. arXiv:1009.1652
 . doi:10.1088/0004-637X/722/1/343.
. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/722/1/343.
- ^ Raassen, A. J. J.; Ness, J.-U.; Mewe, R.; Van Der Meer, R. L. J.; Burwitz, V.; Kaastra, J. S. (2003). „Chandra-LETGS X-ray observation of α Centauri: A nearby (G2V + K1V) binary system”. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 400 (2): 671—678. Bibcode:2003A&A...400..671R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021899
 .
.
- ^ Joyce, M.; Chaboyer, B. (2018). „Classically and Asteroseismically Constrained 1D Stellar Evolution Models of α Centauri a and B Using Empirical Mixing Length Calibrations”. The Astrophysical Journal. 864 (1): 99. Bibcode:2018ApJ...864...99J. arXiv:1806.07567
 . doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aad464.
. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aad464.
- ^ Pourbaix, D.; et al. (2002). „Constraining the difference in convective blueshift between the components of alpha Centauri with precise radial velocities”. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 386 (1): 280—285. Bibcode:2002A&A...386..280P. arXiv:astro-ph/0202400
 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020287.
. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020287.
- ^ Henderson, H. (1839). „On the parallax of α Centauri” (PDF). Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 4 (19): 168—169. Bibcode:1839MNRAS...4..168H. doi:10.1093/mnras/4.19.168.
- ^ Henderson, T. (1842). „The Parallax of α Centauri, deduced from Mr. Maclear's Observations at the Cape of Good Hope, in the Years 1839 and 1840”. Memoirs of the Royal Astronomical Society. 12: 370—371. Bibcode:1842MmRAS..12..329H.
- ^ Maclear, T. (1851). „Determination of the Parallax of α 1 and α2 Centauri, from Observations made at the Royal Observatory, Cape of Good Hope, in the Years 1842-3-4 and 1848”. Memoirs of the Royal Astronomical Society. 20: 98. Bibcode:1851MmRAS..20...70M.
- ^ Moesta, C. G. (1868). „Bestimmung der Parallaxe von α und β Centauri” [Determining the parallax of α and β Centauri]. Astronomische Nachrichten (na jeziku: German). 71 (8): 117—118. Bibcode:1868AN.....71..113M. doi:10.1002/asna.18680710802.
- ^ Gill, David; Elkin, W.L. (1885). „Heliometer-Determinations of Stellar Parallax in the Southern Hemisphere”. Memoirs of the Royal Astronomical Society. 48: 188. Bibcode:1885MmRAS..48....1G.
- ^ Roberts, Alex W. (1895). „Parallax of α Centauri from Meridian Observations 1879–1881”. Astronomische Nachrichten. 139 (12): 189—190. Bibcode:1895AN....139..177R. doi:10.1002/asna.18961391202.
- ^ Woolley, R.; Epps, E. A.; Penston, M. J.; Pocock, S. B. (1970). „Woolley 559”. Catalogue of Stars within 25 Parsecs of the Sun. 5: ill. Bibcode:1970ROAn....5.....W. Arhivirano iz originala 08. 10. 2017. g. Pristupljeno 9. 5. 2014.
- ^ Gliese, W.; Jahreiß, H. (1991). „Gl 559”. Preliminary Version of the Third Catalogue of Nearby Stars. Astronomische Rechen-Institut. Pristupljeno 9. 5. 2014.
- ^ Van Altena, W. F.; Lee, J. T.; Hoffleit, E. D. (1995). „GCTP 3309”. The General Catalogue of Trigonometric Stellar Parallaxes (Fourth izd.). Yale University Observatory. Pristupljeno 9. 5. 2014.
- ^ Perryman; et al. (1997). „HIP 71683”. The Hipparcos and Tycho Catalogues. Pristupljeno 9. 5. 2014.
- ^ Perryman; et al. (1997). „HIP 71683”. The Hipparcos and Tycho Catalogues. Pristupljeno 9. 5. 2014.
- ^ Perryman; et al. (1997). „HIP 71681”. The Hipparcos and Tycho Catalogues. Pristupljeno 9. 5. 2014.
- ^ Perryman; et al. (1997). „HIP 71681”. The Hipparcos and Tycho Catalogues. Pristupljeno 9. 5. 2014.
- ^ Söderhjelm, Staffan (1999). „HIP 71683”. Visual binary orbits and masses post Hipparcos. Pristupljeno 9. 5. 2014.
- ^ van Leeuwen, Floor (2007). „HIP 71683”. Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction.
- ^ van Leeuwen, Floor (2007). „HIP 71681”. Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction.
- ^ „The One Hundred Nearest Star Systems”. Research Consortium On Nearby Stars. Georgia State University. 7. 9. 2007. Arhivirano iz originala 12. 11. 2007. g. Pristupljeno 2. 12. 2014.
Spoljašnje veze
[uredi | uredi izvor]- SIMBAD observational data
- Sixth Catalogue of Orbits of Visual Binary Stars U.S.N.O.
- The Imperial Star – Alpha Centauri
- Alpha Centauri – A Voyage to Alpha Centauri
- Immediate History of Alpha Centauri
- eSky : Alpha Centauri
Hipotetične planete ili eksploracija
[uredi | uredi izvor]- „A Family Portrait of the Alpha Centauri System”. SpaceRef.com: 5. 2003. Bibcode:2003eso..pres....5. Pristupljeno 21. 3. 2003.[mrtva veza]
- Alpha Centauri System
- O Sistema Alpha Centauri (Portuguese) Архивирано на сајту Wayback Machine (3. март 2016)
- Alpha Centauri – Associação de Astronomia (Portuguese)
- Thompson, Andrea (7. 3. 2008). „Nearest Star System Might Harbor Earth Twin”. SPACE.com. Arhivirano iz originala 2. 6. 2008. g. Pristupljeno 17. 7. 2008.
