Južna kruna (sazvežđe)
| Sazvežđe | |
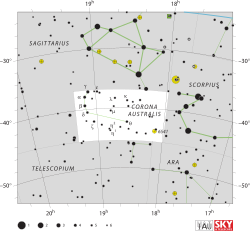 | |
| Latinsko ime | Corona Australis |
|---|---|
| Skraćenica | CrA |
| Genitiv | Coronae Australis / Coronae Austrinae[1][2][3] |
| Simbolizuje | Dionisova kruna |
| Rektascenzija | 19[4] |
| Deklinacija | -40[4] |
| Površina | 128 sq. deg. (80) |
| Najsjajnija zvezda | Alfa Južne krune (4,10m) |
| Meteorski rojevi | nema |
| Susedna sazvežđa | |
| Vidljivo u rasponu +40° i −90°. U najboljem položaju za posmatranje u 21:00 čas u avgustu.  | |
Južna kruna (lat. Corona Australis) je jedno od 88 modernih i 48 originalnih Ptolemejevih sazvežđa. Pre Ptolemeja nije smatrano za posebno sazvežđe, već samo za asterizam u Strelcu.
Zvezde
[uredi | uredi izvor]U južnoj kruni nema zvezda sjajnijih od četvrte magnitude. Najsjajnije su alfa i beta Južne krune, megnitude 4,11. Alfa je i jedina zvezda ovog sazvežđa sa ličnim imenom — Alfeka meridijana.
U Južnoj kruni se nalazi i jedna od najbližih (na oko 200 svetlosnih godina) neutronskih zvezda — RX J1856.5-3754 — za koju se smatra da je nastala u eksploziji supernove pre oko milion godina.
Gama, kapa i lambda Južne krune su binarne zvezde.
Objekti dubokog neba
[uredi | uredi izvor]Na pola puta između tete Južne krune i tete Škorpije se nalazi NGC 6541 — veliko, svetlo globularno jato. NGC 6729 je kombinacija refleksione i emisione magline koja se nalazi oko promenljive zvezde R Južne krune.
Reference
[uredi | uredi izvor]- ^ Bagnall 2012, str. 170.
- ^ „Corona”. Merriam-Webster Dictionary., „Australis”. Merriam-Webster Dictionary..
- ^ „Corona Australis”. Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House.
- ^ a b IAU, The Constellations, Corona Australis.
Literatura
[uredi | uredi izvor]- Allen, Richard Hinckley (1963) [1899]. Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (reprint izd.). New York, NY: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-21079-7.
- Bagnall, Philip M. (2012). The Star Atlas Companion : What you need to know about the Constellations. Springer New York. ISBN 978-1-4614-0830-7.
- Bakich, Michael E. (1995). The Cambridge Guide to the Constellations. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-44921-2.
- Bakich, Michael E. (2010). 1,001 Celestial Wonders to See Before You Die. Springer Science + Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4419-1777-5.
- Coe, Steven R. (2007). Nebulae and how to observe them. Astronomers' observing guides. New York, New York: Springer. ISBN 978-1-84628-482-3.
- Drake, Jeremy J.; Marshall, Herman L.; Dreizler, Stefan; Freeman, Peter E.; Fruscione, Antonella; Juda, Michael; Kashyap, Vinay; Nicastro, Fabrizio; Pease, Deron O.; Wargelin, Bradford J.; Werner, Klaus (jun 2002). „Is RX J1856.5−3754 a Quark Star?”. The Astrophysical Journal. 572 (2): 996—1001. Bibcode:2002ApJ...572..996D. S2CID 18481546. arXiv:astro-ph/0204159
 . doi:10.1086/340368.
. doi:10.1086/340368. - Ellyett, C. D.; Keay, C. S. L. (1956). „Radio Echo Observations of Meteor Activity in the Southern Hemisphere”. Australian Journal of Physics. 9 (4): 471—480. Bibcode:1956AuJPh...9..471E. doi:10.1071/PH560471
 .
. - Falkner, David E. (2011). The Mythology of the Night Sky: An Amateur Astronomer's Guide to the Ancient Greek and Roman Legends. New York, New York: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4614-0136-0.
- Griffiths, Martin (2012). Planetary Nebulae and How to Observe Them. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4614-1781-1.
- Hamacher, Duane W.; Frew, David J. (2010). „An Aboriginal Australian Record of the Great Eruption of Eta Carinae”. Journal of Astronomical History & Heritage. 13 (3): 220—234. Bibcode:2010JAHH...13..220H. arXiv:1010.4610
 .
. - Ho, W. C. G.; Kaplan, D. L.; Chang, P.; Van Adelsberg, M.; Potekhin, A. Y. (mart 2007). „Magnetic hydrogen atmosphere models and the neutron star RX J1856.5–3754”. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 375 (3): 821—830. Bibcode:2007MNRAS.375..821H. S2CID 2046995. arXiv:astro-ph/0612145v1
 . doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11376.x.
. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11376.x. - Jenniskens, Peter (jul 1994). „Meteor stream activity I. The annual streams”. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 287: 990—1013. Bibcode:1994A&A...287..990J.
- Jopek, T. J.; Koten, P.; Pecina, P. (maj 2010). „Meteoroid streams identification amongst 231 Southern hemisphere video meteors”. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 404 (2): 867—875. Bibcode:2010MNRAS.404..867J. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16316.x
 .
. - Makemson, Maud Worcester (1941). The Morning Star Rises: an account of Polynesian astronomy. Yale University Press. Bibcode:1941msra.book.....M.
- Malin, David; Frew, David J. (1995). Hartung's Astronomical Objects for Southern Telescopes: A Handbook for Amateur Observers. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-55491-6.
- Malin, David (avgust 2010). „The Corona Australis nebula (NGC 6726-27-29)”. Australian Astronomical Observatory. Arhivirano iz originala 30. 9. 2012. g. Pristupljeno 4. 7. 2012.
- Moore, Patrick; Tirion, Wil (1997). Cambridge Guide to Stars and Planets. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-58582-8.
- Moore, Patrick (2000). The Data Book of Astronomy. Institute of Physics Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7503-0620-1.
- Moore, Patrick (2000). Stargazing: Astronomy without a Telescope
 . Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-79445-9.
. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-79445-9. - Moore, Patrick (2005). The Observer's Year: 366 Nights of the Universe. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-884-8.
- Moore, Patrick; Rees, Robin (2011). Patrick Moore's Data Book of Astronomy. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-04070-9.
- Motz, Lloyd; Nathanson, Carol (1988). The Constellations. New York City: Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-385-17600-2.
- Motz, Lloyd; Nathanson, Carol (1991). The Constellations: An Enthusiast's Guide to the Night Sky. London, United Kingdom: Aurum Press. ISBN 978-1-85410-088-7.
- O'Meara, Stephen James (2002). The Caldwell Objects. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-82796-6.
- O'Meara, Stephen James (2011). Deep-Sky Companions: The Secret Deep. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-19876-9.
- Porter, Deborah Lynn (1996). From Deluge to Discourse: Myth, History, and the Generation of Chinese Fiction. Albany, New York: SUNY Press. ISBN 978-0-7914-3034-7.
- Reipurth, Bo, ur. (2008). „The Corona Australis Star Forming Region”. Handbook of Star Forming Regions. II: The Southern Sky. ASP Monograph Publications. Bibcode:2008hsf2.book..735N.
- Ridpath, Ian; Tirion, Wil (2017). Stars and Planets Guide (5th ed.). Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-69-117788-5.
- Rogers, J. H. (1998). „Origins of the ancient constellations: I. The Mesopotamian traditions”. Journal of the British Astronomical Association. 108 (1): 9—28. Bibcode:1998JBAA..108....9R.
- Rogers, L. J.; Keay, C. S. L. (1993). Stohl, J.; Williams, I.P., ur. „Observations of some southern hemisphere meteor showers”. Meteoroids and Their Parent Bodies, Proceedings of the International Astronomical Symposium Held at Smolenice, Slovakia, July 6–12, 1992: 273—276. Bibcode:1993mtpb.conf..273R.
- Royer, F.; Zorec, J.; Gómez, A.E. (februar 2007). „Rotational velocities of A-type stars. III. Velocity distributions”. Astronomy & Astrophysics. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 463 (2): 671—682. Bibcode:2007A&A...463..671R. S2CID 18475298. arXiv:astro-ph/0610785
 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065224.
. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065224. - Russell, Henry Norris (oktobar 1922). „The new international symbols for the constellations”. Popular Astronomy. 30: 469. Bibcode:1922PA.....30..469R.
- Sherrod, P. Clay; Koed, Thomas L. (2003). A Complete Manual of Amateur Astronomy: Tools and Techniques for Astronomical Observations. Courier Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-42820-8.
- Simpson, Phil (2012). Guidebook to the Constellations : Telescopic Sights, Tales, and Myths. Springer New York. ISBN 978-1-4419-6940-8.
- Staal, Julius D. W. (1988). The New Patterns in the Sky: Myths and Legends of the Stars. McDonald and Woodward Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-939923-04-5.
- Steinicke, Wolfgang (2010). Observing and Cataloging Nebulae and Star Clusters: From Herschel to Dreyer. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-19267-5.
- Wagman, Morton (2003). Lost Stars: Lost, Missing and Troublesome Stars from the Catalogues of Johannes Bayer, Nicholas Louis de Lacaille, John Flamsteed, and Sundry Others. Blacksburg, VA: The McDonald & Woodward Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-939923-78-6.
- Wang, Hongchi; Mundt, Reinhard; Henning, Thomas; Apai, Dániel (20. 12. 2004). „Optical Outflows in the R Coronae Australis Molecular Cloud” (PDF). The Astrophysical Journal. 617 (2): 1191—1203. Bibcode:2004ApJ...617.1191W. doi:10.1086/425493. Arhivirano iz originala (PDF) 28. 10. 2005. g.
- Weiss, A. A. (1957). „Meteor Activity in the Southern Hemisphere”. Australian Journal of Physics. 10 (2): 299—308. Bibcode:1957AuJPh..10..299W. doi:10.1071/PH570299
 .
. - „AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 7 月 2 日” (na jeziku: kineski). 2006. Arhivirano iz originala 16. 07. 2011. g. Pristupljeno 15. 7. 2012.
- Bakich, Michael E. (25. 6. 2009). „Podcast: Night-sky targets for June 26 – July 3, 2009”. Astronomy. Pristupljeno 21. 8. 2012. (potrebna pretplata)
- Bakich, Michael E. (26. 8. 2010). „Observing podcast: Corona Australis, the Castaway Cluster, and the Red Spider Nebula”. Pristupljeno 21. 8. 2012. (potrebna pretplata)
- Bakich, Michael E. (18. 8. 2011). „Open cluster M26, globular cluster M56, and spiral galaxy IC 4808”. Astronomy. Pristupljeno 21. 8. 2012. (potrebna pretplata)
- Bakich, Michael E. (5. 7. 2012). „Globular cluster NGC 6541, planetary nebula NGC 6563, and irregular galaxy IC 4662”. Astronomy. Pristupljeno 21. 8. 2012. (potrebna pretplata)
- Hamacher, Duane (28. 3. 2011). „Impact Craters in Aboriginal Dreamings, Part 2: Tnorala (Gosses Bluff)”. Australian Aboriginal Astronomy. Aboriginal Astronomy Project. Pristupljeno 24. 9. 2012.
- „Corona Australis, constellation boundary”. The Constellations. International Astronomical Union. Pristupljeno 3. 7. 2012.
- Kaler, Jim. „Alfecca Meridiana”. Stars. University of Illinois. Pristupljeno 15. 8. 2012.
- Kaler, Jim. „Beta Coronae Australis”. Stars. University of Illinois. Pristupljeno 5. 7. 2012.
- Kaler, Jim. „Epsilon Coronae Australis”. Stars. University of Illinois. Pristupljeno 5. 7. 2012.
- Jet Propulsion Laboratory (2011). „Classifications for NGC 6768: 2 Classifications found in NED”. NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database. California Institute of Technology/National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Pristupljeno 20. 8. 2012.
- Lloyd, Lucy (11. 10. 1873). „Story: ≠nabbe ta !nu (Corona Australis)”. The Digital Bleek & Lloyd. University of Cape Town. Pristupljeno 16. 8. 2012.
- Ridpath, Ian. „Constellations”. Pristupljeno 25. 8. 2012.
- Ridpath, Ian (1988). „Corona Australis”. Star Tales. Pristupljeno 3. 7. 2012.
- Streicher, Magda (avgust 2008). „The Southern Queen's Crown” (PDF). Deepsky Delights. The Astronomical Society of Southern Africa. Pristupljeno 17. 8. 2012.
- „Alpha Coronae Australis”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 3. 7. 2012.
- „Beta Coronae Australis”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 3. 7. 2012.
- „LTT 7565 (Gamma Coronae Australis)”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 3. 7. 2012.
- „HR 7226 (Gamma Coronae Australis A)”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 3. 7. 2012.
- „HR 7227 (Gamma Coronae Australis B)”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 3. 7. 2012.
- „Epsilon Coronae Australis”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 5. 7. 2012.
- „HR 6953 (Kappa² Coronae Australis)”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 17. 8. 2012.
- „HR 6952 (Kappa¹ Coronae Australis)”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 17. 8. 2012.
- „Lambda Coronae Australis”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 21. 7. 2012.
- „HR 7050 (Mu Coronae Australis)”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 8. 9. 2012.
- „Zeta Coronae Australis”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 9. 7. 2012.
- „Theta Coronae Australis”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 15. 8. 2012.
- „R Coronae Australis”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 4. 7. 2012.
- „TY Coronae Australis”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 6. 7. 2012.
- „RU Coronae Australis”. SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Pristupljeno 11. 7. 2012.
