RGS4
Изглед
| Regulator G-proteinske signalizacije 4 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 1agr. | |||||||||
| Dostupne strukture | |||||||||
| 1agr, 1ezt, 1ezy | |||||||||
| Identifikatori | |||||||||
| Simboli | RGS4; MGC2124; MGC60244; RGP4; SCZD9 | ||||||||
| Vanjski ID | OMIM: 602516 MGI: 108409 HomoloGene: 4100 GeneCards: RGS4 Gene | ||||||||
| |||||||||
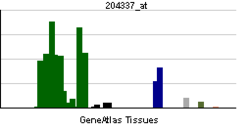
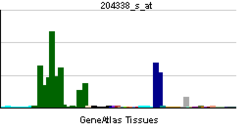
| Pregled RNK izražavanja | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| podaci | |||||||||
| Ortolozi | |||||||||
| Vrsta | Čovek | Miš | |||||||
| Entrez | 5999 | 19736 | |||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000117152 | ENSMUSG00000038530 | |||||||
| UniProt | P49798 | Q5D078 | |||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_005613 | NM_009062 | |||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_005604 | NP_033088 | |||||||
| Lokacija (UCSC) |
Chr 1: 161.31 - 161.31 Mb |
Chr 1: 171.58 - 171.58 Mb | |||||||
| PubMed pretraga | [1] | [2] | |||||||
Regulator G proteinske signalizacije 4 (RGS4) je protein koji reguliše G proteinsku signalizaciju.[1] Brojne sudije su ukazale na vezu RGS4 gena sa šizofrenijom,[2][3][4][5] mada postoje i studije koje nisu ustanovile vezu.[6]
RGS4 je takođe od interesa kao jedan od tri glavna RGS proteina (zajedno sa RGS9 i RGS17) koji učestvuju u terminaciji signalizacije mi opioidnog receptora,[7] i moguće je da je značajan u razvoju tolerancije na opioidne lekove.[8][9][10][11][12]
Inhibitori
[уреди | уреди извор]Interakcije
[уреди | уреди извор]Za RGS4 je pokazano da interaguje sa ERBB3,[15] GNAQ[16][17] i COPB2.[18]
Reference
[уреди | уреди извор]- ^ „Entrez Gene: RGS4 regulator of G-protein signalling 4”.
- ^ Stefanis NC, Trikalinos TA, Avramopoulos D, Smyrnis N, Evdokimidis I, Ntzani EE, Hatzimanolis A, Ioannidis JP, Stefanis CN (2008). „Association of RGS4 variants with schizotypy and cognitive endophenotypes at the population level”. Behavioral and Brain Functions. 4: 46. PMC 2572614
 . PMID 18834502. doi:10.1186/1744-9081-4-46.
. PMID 18834502. doi:10.1186/1744-9081-4-46.
- ^ Prasad KM, Almasy L, Gur RC, Gur RE, Pogue-Geile M, Chowdari KV, Talkowski ME, Nimgaonkar VL (2009). „RGS4 Polymorphisms Associated With Variability of Cognitive Performance in a Family-Based Schizophrenia Sample”. Schizophrenia Bulletin. 36 (5): 983—90. PMC 2930339
 . PMID 19282471. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbp002.
. PMID 19282471. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbp002.
- ^ Dean B, Boer S, Gibbons A, Money T, Scarr E (2009). „Recent advances in postmortem pathology and neurochemistry in schizophrenia”. Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 22 (2): 154—60. PMID 19553869. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e328323d52e.
- ^ Ding L, Hegde AN (2009). „Expression of RGS4 splice variants in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of schizophrenic and bipolar disorder patients”. Biological Psychiatry. 65 (6): 541—5. PMID 19041089. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.10.026.
- ^ Stuart Gibbons A, Scarr E, McOmish CE, Hannan AJ, Thomas EA, Dean B (2008). „Regulator of G-protein signalling 4 expression is not altered in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia”. The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 42 (8): 740—5. PMID 18622782. doi:10.1080/00048670802206338.
- ^ Hooks SB, Martemyanov K, Zachariou V (2008). „A role of RGS proteins in drug addiction”. Biochemical Pharmacology. 75 (1): 76—84. PMID 17880927. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.07.045.
- ^ Grillet N, Pattyn A, Contet C, Kieffer BL, Goridis C, Brunet JF (2005). „Generation and characterization of Rgs4 mutant mice”. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 25 (10): 4221—8. PMC 1087729
 . PMID 15870291. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.10.4221-4228.2005.
. PMID 15870291. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.10.4221-4228.2005.
- ^ Garzón J, Rodríguez-Muñoz M, de la Torre-Madrid E, Sánchez-Blázquez P (2005). „Effector antagonism by the regulators of G protein signalling (RGS) proteins causes desensitization of mu-opioid receptors in the CNS”. Psychopharmacology. 180 (1): 1—11. PMID 15830230. doi:10.1007/s00213-005-2248-9.
- ^ Georgoussi Z, Leontiadis L, Mazarakou G, Merkouris M, Hyde K, Hamm H (2006). „Selective interactions between G protein subunits and RGS4 with the C-terminal domains of the mu- and delta-opioid receptors regulate opioid receptor signaling”. Cellular Signalling. 18 (6): 771—82. PMID 16120478. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.07.003.
- ^ Leontiadis LJ, Papakonstantinou MP, Georgoussi Z (2009). „Regulator of G protein signaling 4 confers selectivity to specific G proteins to modulate mu- and delta-opioid receptor signaling”. Cellular Signalling. 21 (7): 1218—28. PMID 19324084. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.03.013.
- ^ Wang Q, Liu-Chen LY, Traynor JR (2009). „Differential Modulation of {micro}- and {delta}-Opioid Receptor Agonists by Endogenous RGS4 Protein in SH-SY5Y Cells”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (27): 18357—67. PMID 19416973. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.015453.
- ^ Jin Y, Zhong H, Omnaas JR, Neubig RR, Mosberg HI (2004). „Structure-based design, synthesis, and activity of peptide inhibitors of RGS4 GAP activity”. Methods in Enzymology. 389: 266—77. PMID 15313571. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(04)89016-5.
- ^ Roman DL, Talbot JN, Roof RA, Sunahara RK, Traynor JR, Neubig RR (2007). „Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of RGS4 using a high-throughput flow cytometry protein interaction assay”. Molecular Pharmacology. 71 (1): 169—75. PMID 17012620. doi:10.1124/mol.106.028670.
- ^ Thaminy, Safia; Auerbach Daniel; et al. (2003). „Identification of novel ErbB3-interacting factors using the split-ubiquitin membrane yeast two-hybrid system”. Genome Res. United States. 13 (7): 1744—53. ISSN 1088-9051. PMC 403748
 . PMID 12840049. doi:10.1101/gr.1276503.
. PMID 12840049. doi:10.1101/gr.1276503.
- ^
- ^ Druey, K M; Sullivan B M; et al. (1998). „Expression of GTPase-deficient Gialpha2 results in translocation of cytoplasmic RGS4 to the plasma membrane”. J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 273 (29): 18405—10. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9660808. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.29.18405.
- ^ Sullivan, B M; Harrison-Lavoie K J; et al. (2000). „RGS4 and RGS2 bind coatomer and inhibit COPI association with Golgi membranes and intracellular transport”. Mol. Biol. Cell. UNITED STATES. 11 (9): 3155—68. ISSN 1059-1524. PMC 14982
 . PMID 10982407.
. PMID 10982407.
Literatura
[уреди | уреди извор]- Levitt P; Ebert P; Mirnics K; et al. (2006). „Making the case for a candidate vulnerability gene in schizophrenia: Convergent evidence for regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4).”. Biol. Psychiatry. 60 (6): 534—7. PMID 16860780. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.04.028.
- Druey KM, Blumer KJ, Kang VH, Kehrl JH (1996). „Inhibition of G-protein-mediated MAP kinase activation by a new mammalian gene family.”. Nature. 379 (6567): 742—6. PMID 8602223. doi:10.1038/379742a0.
- Berman DM, Wilkie TM, Gilman AG (1996). „GAIP and RGS4 are GTPase-activating proteins for the Gi subfamily of G protein alpha subunits.”. Cell. 86 (3): 445—52. PMID 8756726. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80117-8.
- Heximer SP; Watson N; Linder ME; et al. (1998). „RGS2/G0S8 is a selective inhibitor of Gqalpha function.”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (26): 14389—93. PMC 24991
 . PMID 9405622. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.26.14389.
. PMID 9405622. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.26.14389. - Srinivasa SP, Bernstein LS, Blumer KJ, Linder ME (1998). „Plasma membrane localization is required for RGS4 function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (10): 5584—9. PMC 20421
 . PMID 9576926. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.10.5584.
. PMID 9576926. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.10.5584. - Druey KM; Sullivan BM; Brown D; et al. (1998). „Expression of GTPase-deficient Gialpha2 results in translocation of cytoplasmic RGS4 to the plasma membrane.”. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (29): 18405—10. PMID 9660808. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.29.18405.
- Faraone SV; Matise T; Svrakic D; et al. (1998). „Genome scan of European-American schizophrenia pedigrees: results of the NIMH Genetics Initiative and Millennium Consortium.”. Am. J. Med. Genet. 81 (4): 290—5. PMID 9674973. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980710)81:4<290::AID-AJMG3>3.0.CO;2-Y.
- Wang J; Ducret A; Tu Y; et al. (1998). „RGSZ1, a Gz-selective RGS protein in brain. Structure, membrane association, regulation by Galphaz phosphorylation, and relationship to a Gz gtpase-activating protein subfamily.”. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (40): 26014—25. PMID 9748280. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.40.26014.
- Shaw SH; Kelly M; Smith AB; et al. (1998). „A genome-wide search for schizophrenia susceptibility genes.”. Am. J. Med. Genet. 81 (5): 364—76. PMID 9754621. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980907)81:5<364::AID-AJMG4>3.0.CO;2-T.
- Posner BA; Mukhopadhyay S; Tesmer JJ; et al. (1999). „Modulation of the affinity and selectivity of RGS protein interaction with G alpha subunits by a conserved asparagine/serine residue.”. Biochemistry. 38 (24): 7773—9. PMID 10387017. doi:10.1021/bi9906367.
- Tu Y, Popov S, Slaughter C, Ross EM (2000). „Palmitoylation of a conserved cysteine in the regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) domain modulates the GTPase-activating activity of RGS4 and RGS10.”. J. Biol. Chem. 274 (53): 38260—7. PMID 10608901. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.53.38260.
- Moy FJ; Chanda PK; Cockett MI; et al. (2000). „1H, 15N, 13C, and 13CO assignments and secondary structure determination of RGS4.”. J. Biomol. NMR. 15 (4): 339—40. PMID 10685342. doi:10.1023/A:1008343609739.
- Popov SG, Krishna UM, Falck JR, Wilkie TM (2000). „Ca2+/Calmodulin reverses phosphatidylinositol 3,4, 5-trisphosphate-dependent inhibition of regulators of G protein-signaling GTPase-activating protein activity.”. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (25): 18962—8. PMID 10747990. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001128200.
- Ekelund J; Lichtermann D; Hovatta I; et al. (2000). „Genome-wide scan for schizophrenia in the Finnish population: evidence for a locus on chromosome 7q22.”. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9 (7): 1049—57. PMID 10767329. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.7.1049.
- Brzustowicz LM; Hodgkinson KA; Chow EW; et al. (2000). „Location of a major susceptibility locus for familial schizophrenia on chromosome 1q21-q22.”. Science. 288 (5466): 678—82. PMID 10784452. doi:10.1126/science.288.5466.678.
- Chatterjee TK, Fisher RA (2000). „Cytoplasmic, nuclear, and golgi localization of RGS proteins. Evidence for N-terminal and RGS domain sequences as intracellular targeting motifs.”. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (31): 24013—21. PMID 10791963. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002082200.
- Chatterjee TK, Fisher RA (2000). „Novel alternative splicing and nuclear localization of human RGS12 gene products.”. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (38): 29660—71. PMID 10869340. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000330200.
- Sullivan BM; Harrison-Lavoie KJ; Marshansky V; et al. (2000). „RGS4 and RGS2 bind coatomer and inhibit COPI association with Golgi membranes and intracellular transport.”. Mol. Biol. Cell. 11 (9): 3155—68. PMC 14982
 . PMID 10982407.
. PMID 10982407. - Dowal L; Elliott J; Popov S; et al. (2001). „Determination of the contact energies between a regulator of G protein signaling and G protein subunits and phospholipase C beta 1.”. Biochemistry. 40 (2): 414—21. PMID 11148035. doi:10.1021/bi001923.
- Richardson RM, Marjoram RJ, Barr AJ, Snyderman R (2001). „RGS4 inhibits platelet-activating factor receptor phosphorylation and cellular responses.”. Biochemistry. 40 (12): 3583—8. PMID 11297424. doi:10.1021/bi0019242.